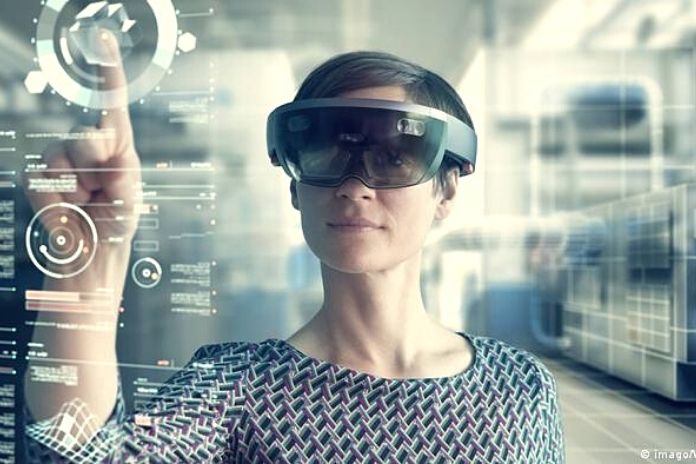
In the new metaverse, it is necessary to take the essential precautions to secure privacy and digital identity. We hear more and more of the metaverse, that is, the future Internet in which we will interact through avatars in totally digital worlds. The word metaverse comes from the combination of the words meta and universe. Inside, users can perform almost the same actions in the real world thanks to avatars: communicate, work, shop, and inform themselves.
For its realization, augmented reality ( AR ) and virtual reality ( VR) create users’ digital identities. Users need to seriously consider the impact cyber threats can have on privacy and their digital identity. The protection of privacy consists precisely in controlling one’s data and how third-parties use them. The cybercriminals could use them to get around their victims, extort or steal their money through the bank details or credit cards linked to accounts.
Metaverse: How It Is Made And What To Expect
The metaverse is possible thanks to augmented reality ( AR ) and virtual reality ( VR ) technologies, apparently very similar terms but with a very different meaning. Augmented reality combines real-world digital elements. The most famous example is the Pokémon Go game, which uses the smartphone screen and its camera to simulate the presence of objects, animated and otherwise, in the surrounding environment.
Virtual reality, instead, does not correlate with the natural world and is made up of an entirely fictitious environment. It is necessary to use particular tools such as a helmet or visor to access it. There is also another variant: it is called mixed reality ( MR ) and represents a sort of evolution of augmented reality. It allows virtual 3D objects to interact with their surroundings physically. For a clearer picture of this type of scenario, you can think of a Pokémon jumping on the sofa in your living room, just like a cat or a dog would.
The IT giants are investing a lot of resources in these technologies to transform these spaces into habitual environments where people can interact and buy objects that have no value. Among the most notable examples of metaverse today, there are:
- MMORPGs.
- A role-playing video game that allows people to play together as characters.
- The three-dimensional worlds of Second Life and Active Worlds.
Although Facebook seems to want to take this path, as confirmed by the recent name change to Meta.
What Are The Privacy Risks?
AR and VR technologies can both put users’ privacy at serious risk, but they do it in a slightly different way, precisely by their other functions. Both can collect highly confidential data and information:
- The AR records identity information and monitors user actions
- VR records biometric data, such as fingerprints, retinal scans, face shape, and so on
In particular, if the hacker was to access an AR device, he could use spoofing to impersonate another person and push the user to do something, or sniffing, to intercept data in transit. Another frequent threat is social engineering, whose name derives from the behavior of the attacker who behaves like a social engineer: he analyzes his victim, collects all the necessary information, and uses his weaknesses to take action. This could involve infecting the victim’s device with malware, stealing confidential data, ransomware, demanding ransom payments, or stealing credentials and payment details.
Among the most common variants of social engineering, attacks are catfishing, which uses a false identity to deceive the person, stalking, whose purpose is to persecute them, and doxing, with which private information is spread online or other sensitive data. Also not to be underestimated is hijacking, a technique with which criminals modify TCP / IP protocol packets to redirect the victim to a web page other than the one they are looking for. If, on the one hand, this allows him to increase visits, and therefore advertising earnings, on the other hand, it can push the victim to enter passwords or confidential information.
In addition to the loss of large sums of money, the consequences for those who underestimate these threats can include the theft of one of the most precious assets: their digital identity. Cybercriminals could, for example, seize the avatar used by the victim in the metaverse and use it to ask for a ransom or to carry out fraud, which would negatively impact the individual’s reputation.
Furthermore, these accounts are often used to buy virtual items, sometimes very expensive, and it is possible to steal cryptocurrency from the wallets linked to them. On the other hand, hackers can use the biometric data captured by VR headsets to obtain PINs and passwords typed with their fingers or create deepfakes using machine learning technologies, which can also record the shape of the face. This would allow them to carry out dangerous ransomware and social engineering attacks more effectively.
How To Protect Your Digital Identity
While hackers can take advantage of different methods to access confidential information, some best practices keep privacy and digital identity safe. The first seems a bit obvious, but it is good to reiterate it: you should never disclose too much personal information that it is not necessary to disclose. As dull as they may appear, you should always read the privacy policies and the ” terms and conditions ” page to be aware of how companies, particularly the platforms that take advantage of AR or VR technologies, store and use our data. It is not excluded that they are shared with third-party companies without the user knowing it.
Another good practice is to use a VPN service and use the virtual private network to keep the identity safe and make it impossible for anyone to track their movements on the Web. Thanks to its use, an encrypted virtual tunnel will be created between the device you browse and the Internet. In particular, the device will assume a fictitious and easily modifiable IP address assigned by the VPN server to which you connect through the Client application. This kind of service is very functional to prevent Man-in-the-Middle attacks that exploit the interception of online communications.
It is always good to keep updated the operating system of any electronic device because it improves the user experience and mainly because they resolve security flaws. When using VR headsets or AR devices, you must constantly update their firmware because otherwise, it is possible to suffer dangerous privacy violations. Of fundamental importance, then, is the use of complex passwords, which are not easily decipherable, and their continuous updating. By using the same short combination for all kinds of accounts, you risk putting any personal information in serious jeopardy.
Two-factor authentication should also be used, which adds an extra degree of security. There are numerous authenticators on smartphones, which are easily configurable in a few steps: they allow you to obtain a code, always different and which can only be known by the owner of the account, to be entered immediately after username and password. Last but not in order of importance is the contribution of good antivirus software, which supports protection during online browsing and defends your operating system from all types of common threats: viruses, malware, ransomware, spyware, phishing, and much more.
Also Read: How To Install WordPress Locally