What Is Big Data?
Huge information is characterized as high volume, fast, and high assortment data (information) assets; they require creative and financially savvy devices for their administration and handling that further develop independent direction and advance interaction mechanization. Huge information is high-volume, high-speed, and high-assortment data resources that request savvy, creative types of data handling that empower upgraded understanding, independent direction, and cycle robotization.
This definition, be that as it may, isn’t adequate to offer a total picture of the “Enormous Data peculiarity”: it isn’t simply an issue of buying and overseeing a lot of information. The change occurring is more profound. The entire course of information assortment, the board, and use changes, the advances supporting the information life cycle advance, and, simultaneously, new jobs and abilities create, for instance, that of Data Scientist and Data Engineer. Moreover, it isn’t to have them accessible to discuss Big Data. The organization design, obtaining, and executive processes should be sufficient.
There has been a noticeable expansion in the creation of Big Data as of late. Organizations could before long create zettabytes of information (billions of terabytes) coming from sensors, satellites, monetary instruments, phones, and so on. Then again, regardless of whether the term Big Data, deciphered as “large information,” is primarily connected to the tremendous volume of information, organized and in any case, in actuality, how much information is significant, however, it is additionally different characteristics, like speed and assortment which we will see later.
In our day to day routine, we are persistently in touch with Big Data, as illustrated, for instance, by the proposal frameworks utilized by Netflix and Amazon, which, in close to ongoing, examine the acquisition of all clients and contrast them and their interests and the hunts of every individual to recommend that they check out (or purchase) items by their preferences. In different areas, for instance, in the monetary one, a few organizations have found that they can assess the monetary gamble by taking advantage of certain information mining research because of the examination of strange ways of behaving.
Why Is Big Data Important?
Knowing how to oversee Big Data proficiently by carrying out a decent Big Data Analytics interaction can affect the progress of organizations in all areas. The transversality of Big Data Analytics is connected to similar qualities of Big Data. Hence, it acquires advantages to all areas with a substantial effect on all periods of the creation cycle and corporate key arrangements. For this equivalent explanation, it isn’t difficult to evaluate the advantages univocally. They are different, starting with one area then onto the next. In general, however, we can identify 3 families of advantages:
- Quantifiable advantages from an economic point of view;
- Quantifiable benefits from the point of view of performance and performance;
- Benefits are not formally quantifiable but measurable as qualitative indicators.
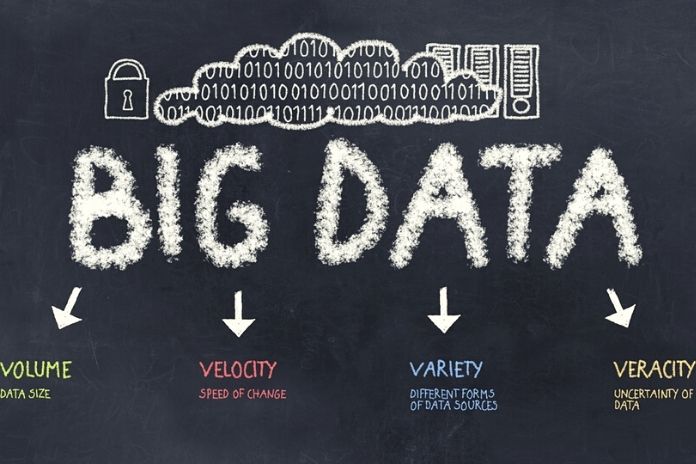
The Five Vs. Of Big Data
The 3Vs: Volume, Speed , and Variety. It is a straightforward model to characterize this “new information” created by the expansion in sources and advances.
Volume
That is how much information is delivered. Because of the bewildering expansion in the gadgets that produce information, an enormous measure of data is continually developing. To give a quantitative sign, we can discuss Big Data when volumes develop by half consistently or when the edge of 50 terabytes is surpassed.
Consider how much data is created by online media clients, the log information delivered by modern hardware, or in any event, banking exchanges, developments in the monetary business sectors. Volumes of this sort can’t be made with conventional apparatuses. For that reason, with regards to Big Data, it is simply correct and important to manage advancements and devices that grew impromptu.
Speed
Firmly connected with huge volumes is the unconventional attribute of speed. It wouldn’t be imaginable to have such a lot of information off chance that creation was not incredibly quick. Additionally, in this sense, it is crucial to utilize satisfactory devices to block and store Big Data accurately, constantly, without misfortunes, and with an assurance of information quality.
The quality of speed can be declined in two ways, not just the speed of creation of Big Data yet additionally the speed of the board and examination of the equivalent: the greatest test as of now for organizations isn’t simply having the option to gather this information yet most importantly to investigate them on schedule to settle on business choices expeditiously because “time is cash.”
Variety
Indeed, even the idea of assortment can be declined in various ways: as a matter of fact, reference is made not exclusively to the various sorts of information accessible for each source, for example, text content, photographs, recordings, reports, in this way organized and unorganized information yet additionally to an assortment of the actual sources, for instance, value-based frameworks, the executive’s frameworks, interpersonal organizations, sites, available information, sensors.
What’s more, that and the missing data or data going with those gathered is recuperated by incorporating various information and various sources. Along these lines, the intricacy of the executives increases dramatically, and here as well, the requirement for sufficient advancements and apparatuses arises. The wide assortment of information accessible additionally prompts the issue of contextualizing the information to give each the proper weight and importance: the translation of information differs as per the source and the setting where it is gathered.
This is a significant stage, particularly in the cutting-edge reality where fake news is at the front of the day, and the speed of data builds its dissemination. From 2001 to the current day, the circumstance has additionally transformed; it has advanced so much that today Laney’sLaney’s underlying 3V worldview appears to be restricted in the meaning of Big Data. From the 3Vs, the worldview has been advanced with numerous factors, including other 2Vs: Truthfulness and Value.
Truthfulness
That is the dependability of the sources. Industry specialists normally say, “Awful information is more terrible than no information.” Big Data is currently a corporate resource. They should be solid and honest, a test, the last option significantly more challenging to manage than when the information didn’t have the current volume, speed, and assortment. Then again, nonetheless, the quality and respectability of data stay a fundamental support point since it impacts the exactness of the examination.
Value
We have as of now composed that Big Data is the new corporate resource, the new oil, a significant wellspring of significant worth for organizations. Gathering information isn’t to the point of acquiring added esteem. Regardless of whether gathered utilizing the best advancements accessible, the information stays an end in themselves on the off chance that they are not suitably taken advantage of. To do as such, they should be changed into important data that permits organizations to confirm and conceivably adjust their decisions and systems.
Assume the data results from the information investigation process. Information is the following stage when the data is dropped into the business setting and used to settle on information-driven choices and do activities. The people who use data from huge amounts of information gain the upper hand. This last trait of Big Data is firmly connected not exclusively to different qualities but most importantly to Big Data Analytics.
To execute the method involved with extracting information from information and guaranteeing that Big Data is changed into data and information to be utilized in the cycles of organizations specially appointed investigation instruments are required. Returning to the Netflix model, this progression is clear. Consider how much data that client searches and sees consistently and what users conduct means for business choices, like making new happy or cancellations. Other undesirable, fantastic activities additionally decrease the gamble of the surrender of clients.
Also Read: Cyber-Security And Cyber-Resilience: Why Companies Need Both